In today’s hyper-connected digital landscape, businesses face an ever-evolving array of cyber threats. Vulnerabilities within IT systems, applications, and networks provide potential entry points for malicious actors, putting sensitive data, financial resources, and reputations at risk. To address this, organizations must adopt vulnerability remediation as a proactive strategy to mitigate threats and enhance their cybersecurity posture.
This comprehensive guide explores the concept of vulnerability remediation, its importance, and the detailed process businesses can follow to safeguard their digital assets.
What is Vulnerability Remediation?
Vulnerability remediation is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating security vulnerabilities in an organization’s IT infrastructure. It goes beyond merely detecting weak points; it involves systematically addressing them to eliminate or reduce risks to an acceptable level. By employing vulnerability remediation strategies, businesses can strengthen their defenses, ensuring operational continuity and compliance with cybersecurity regulations.
Why is Vulnerability Remediation important for Businesses?
Vulnerability remediation is essential for businesses because it acts as a proactive shield against the constantly evolving landscape of cyber threats. In an era where cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, even minor vulnerabilities in systems, applications, or networks can serve as gateways for malicious actors. Addressing these weaknesses promptly ensures that potential breaches are minimized, safeguarding sensitive data, financial assets, and overall business operations.
Regulatory compliance is another critical driver for vulnerability remediation. Many industries are subject to stringent data protection laws and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, which mandate the identification and remediation of security vulnerabilities. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines, legal consequences, and reputational harm. By effectively managing vulnerabilities, businesses not only adhere to these requirements but also demonstrate a commitment to maintaining robust security practices. A business’s reputation is one of its most valuable assets. A data breach or cyberattack can erode trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders, potentially leading to long-term damage. Proactive vulnerability remediation signals to stakeholders that the organization prioritizes security and takes a responsible approach to protecting its digital assets. This trust is crucial for maintaining strong relationships and staying competitive in the market.
Process involved in Vulnerability Remediation
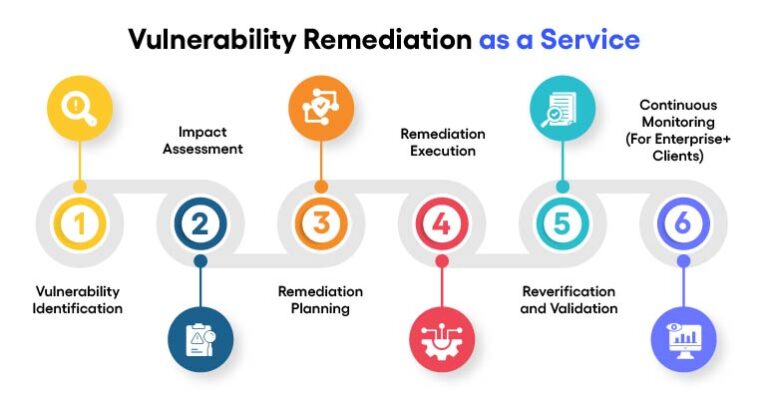
Vulnerability remediation is a structured, multi-step process that ensures a systematic approach to risk mitigation:
1.Vulnerability Identification
The first step is to detect vulnerabilities using tools like vulnerability scanners, penetration testing, and manual assessments. These tools identify weaknesses in applications, networks, endpoints, and databases.
Tools used:
- Nessus
- Qualys
- OpenVAS
- Burp Suite
2. Impact Assessment
After vulnerabilities are identified, the next step is prioritizing them based on their severity, potential impact, and exploitability. The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is often used to classify risks into high, medium, and low categories.
Key considerations:
- How critical is the affected system?
- Could this vulnerability expose sensitive data?
- How easy is it for an attacker to exploit?
3. Remediation Planning
With priorities established, a detailed remediation plan is created. This plan outlines:
- The specific actions to address each vulnerability (e.g., applying patches, reconfiguring systems, or implementing additional security measures).
- A timeline for completing these actions based on the risk level.
Stakeholders involved:
- Security teams
- IT administrators
- Software developers
4. Remediation Execution
The planned steps are implemented, addressing vulnerabilities across systems and networks. Execution might involve:
- Deploying patches.
- Reconfiguring permissions or settings.
- Replacing outdated software or hardware.
Coordination between departments is critical to avoid unintentional disruptions.
5. Reverification and Validation
After execution, systems are re-scanned or retested to ensure vulnerabilities have been successfully addressed. Validation confirms that the applied fixes are effective and that no new issues have been introduced.
Tools for reverification:
- Retesting through automated scanners.
- Manual validation by penetration testers.
6. Continuous Monitoring
For large organizations, vulnerabilities emerge continuously due to changing environments and evolving threats. Continuous monitoring ensures new weaknesses are detected promptly and addressed before exploitation.
Techniques for continuous monitoring:
- Real-time scanning with automated tools.
- Threat intelligence feeds to stay updated on emerging risks.
Common challenges in vulnerability remediation
Despite its critical importance, organizations often face hurdles in implementing an effective vulnerability remediation process:
1.Resource Constraints: Limited staff or budget can hinder remediation efforts.
2. Complex IT Environments: A mix of legacy systems and modern applications complicates vulnerability management.
3. High Volume of Vulnerabilities: Organizations often face thousands of vulnerabilities, making prioritization challenging.
4. Lack of Expertise: Specialized knowledge is required to effectively remediate advanced or unique vulnerabilities.
5. Operational Disruptions: Applying patches or reconfiguring systems can sometimes disrupt business operations.

Best practices for effective vulnerability remediation
To overcome challenges and maximize the effectiveness of vulnerability remediation, businesses should adopt the following best practices:
Conclusion
Vulnerability remediation is a cornerstone of a robust cybersecurity strategy. By systematically identifying, assessing, and addressing vulnerabilities, businesses can protect themselves from potential attacks, ensure compliance, and maintain operational continuity.
While challenges may arise, following a structured remediation process and adopting best practices can help organizations minimize risk and safeguard their assets effectively. Investing in vulnerability remediation is not just a cybersecurity measure; it’s a business imperative.
For tailored vulnerability management and remediation services, consider partnering with a trusted cybersecurity provider like StrongBox IT, ensuring your business stays resilient in an ever-evolving threat landscape.





