Information security, abbreviated as InfoSec, is the process of safeguarding information by mitigating information risks. It’s a component of information risk management. It typically entails preventing or reducing the likelihood of unauthorized/inappropriate data access or the illegal use, disclosure, disruption, deletion, corruption, modification of information.
Information security is achieved through a structured risk management process that includes:
- Identifying information and related assets, as well as potential threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts.
- Evaluating the risks; deciding how to address or treat the risks i.e. to avoid, mitigate, share, or accept them.
- Risk mitigation is required, selecting or designing appropriate security controls and implementing them.
- Monitoring the activities, making adjustments as needed to address any issues, changes, and improvement opportunities.
Information security mainly relies on three pillars
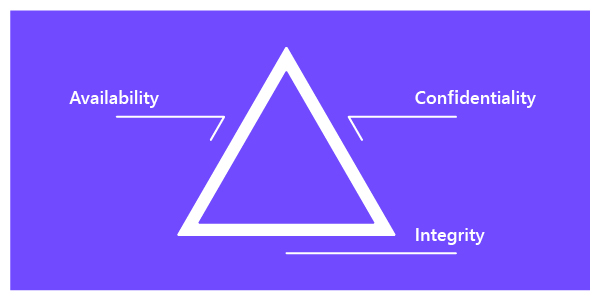
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
Confidentiality
Confidentiality in information security is “the property that information is not made available or disclosed to unauthorized individuals, entities, or processes.” While the terms “privacy” and “security” are similar, they are not interchangeable.

Confidentiality is a component of privacy that we use to protect our data from unauthorized viewers. Password theft, data theft are some of the examples of confidentiality compromise.
Integrity
Data integrity in Information security refers to maintaining and ensuring the accuracy and completeness of data throughout its entire lifecycle. This means that data can’t be corrupted or modified in an unauthorized or undetected way.

Controls to ensure the integrity of information security systems are typically included, with a focus on protecting the kernel or core functions from both deliberate and unintentional threats.
Availability
Any information system must be available when it is needed for it to serve its purpose. For complete availability of the system,
- The computers used to store and process the information
- The access controls used to preserve it.
- The communication channels used to connect it.

Stopping denial-of-service attacks, such as a flood of incoming messages to the target device, which effectively forces it to shut it down, is also part of ensuring availability.
Conclusion
The act of maintaining CIA information, ensuring that information is uncompromised in any way when critical issues arise, is at the heart of information security. These problems are not limited to natural disasters, computer/server failures, and so on.
As a result, in recent years, information security has evolved significantly. There are many opportunities in this field such as securing networks and allied infrastructure, securing applications and databases, security testing, information systems auditing, business continuity planning, etc.





