The banking sector faces an ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, making robust cybersecurity measures a top priority. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has responded to this challenge by establishing comprehensive guidelines for a cybersecurity framework tailored specifically for banks and financial institutions. These guidelines aim to fortify the financial sector against cyber risks, ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of sensitive data and systems. In this blog, we’ll explore the key elements of the RBI’s cybersecurity framework, exploring its purpose, components, and the significant benefits it offers to institutions striving to protect their operations.
What is the RBI cybersecurity framework, and what is its purpose?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) cybersecurity framework is a set of guidelines and standards established by the RBI to enhance the cybersecurity posture of banks and financial institutions in India. The framework is designed to address the growing threats and risks associated with cyberattacks and ensure the safety and security of the banking and financial sector.
Purpose of the RBI Cybersecurity Framework
- Protect Financial Systems: The primary purpose of the framework is to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of financial data and systems from cyber threats.
- Enhance Preparedness: It aims to improve banks’ overall cybersecurity preparedness by ensuring they implement robust security measures and are equipped to respond to and recover from cyber incidents.
- Risk Management: The framework helps banks to identify, assess, and manage cyber risks, ensuring that they have appropriate risk management practices in place.
- Compliance: It ensures that banks and financial sectors comply with regulatory requirements related to cybersecurity, which helps in maintaining trust and confidence among customers and stakeholders.
- Incident Reporting: The framework mandates timely reporting of cybersecurity incidents to the RBI, which helps track and mitigate the impact of cyber threats on the banking sector.
RBI guidelines for cybersecurity framework
The RBI has established a robust cybersecurity framework to protect banks and financial institutions. This framework outlines crucial areas for financial sectors to focus on, promoting a comprehensive and proactive approach to cybersecurity. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key elements of this framework,
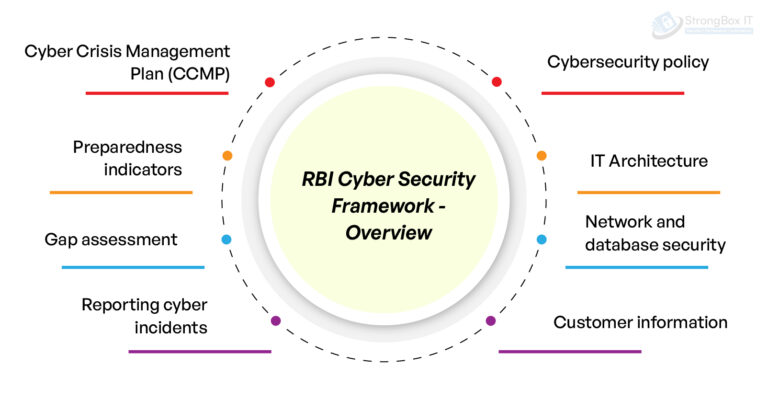
Cybersecurity policy
- Objective: Establish a clear, board-approved policy outlining the approach to managing cyber risks.
- Components: It should include guidelines on risk assessment, control measures, incident response, and continuous monitoring. The policy must be reviewed and updated regularly to address emerging threats.
IT Architecture
- Objective: Implement a secure and resilient IT infrastructure.
- Components: Design IT systems to minimize vulnerabilities, ensure secure configurations, and segregate critical systems to prevent widespread damage from attacks.
Network and database security
- Objective: Protect the integrity and confidentiality of network and database systems.
- Components: Deploy firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, encryption, and access controls. Regularly monitor and audit network traffic and database activities for anomalies.
Customer information
- Objective: Safeguard sensitive customer data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Components: Implement strong authentication mechanisms, encryption of data at rest and in transit, and regular security assessments of systems handling customer information.
Cyber Crisis Management Plan (CCMP)
- Objective: Establish a robust plan to handle cyber incidents effectively.
- Components: Define roles and responsibilities, establish communication protocols, and outline procedures for incident detection, response, and recovery. Regular drills and simulations should be conducted to test the effectiveness of the CCMP.
Preparedness indicators
- Objective: Monitor and evaluate the readiness of the institution to handle cyber threats.
- Components: Develop key performance indicators (KPIs) and key risk indicators (KRIs) to measure cybersecurity readiness. Regularly assess these indicators to identify areas needing improvement.
Gap assessment
- Objective: Identify and address deficiencies in the cybersecurity framework.
- Components: Conduct regular assessments to compare current security measures against industry standards and regulatory requirements. Develop and implement action plans to close identified gaps.
Reporting cyber incidents
- Objective: Ensure timely and accurate reporting of cyber incidents to the appropriate authorities.
- Components: Establish a clear process for reporting incidents to the RBI and other relevant agencies. Maintain records of incidents, responses, and remedial actions taken.
Baseline cybersecurity and resilience framework
For the baseline cyber security and resilience framework, RBI provided explicit guidance for control implementation. The baseline controls are listed as follows:
- Inventory Management of Business
- IT Assets Preventing execution of unauthorized software
- Application Security Life Cycle (ASLC)
- Maintenance, Monitoring, and Analysis of Audit Logs
- Audit Log settings
- Metrics
- Patch/Vulnerability & Change Management
- Vendor Risk Management
- Removable Media
- Forensics
- Environmental Controls
- Network Management and Security
- User Access Control / Management
- Authentication Framework for Customers
- Advanced Real-time Threat Defense and Management
- Anti-Phishing
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Test
- Red Team Exercises
- Secure Configuration
- Secure mail and messaging systems
- Incident Response & Management
- User / Employee/ Management Awareness
- Customer Education and Awareness
- Secure Configuration
- Secure mail and messaging systems
- Data Leak Prevention Strategy
- Risk-based transaction monitoring
Benefits of implementing the RBI cybersecurity framework
Implementing the RBI cybersecurity framework provides numerous benefits to banks and financial institutions. These benefits enhance the overall security posture, operational resilience, and trust in the financial sector. Here are some key advantages:
- Enhanced security: By implementing a comprehensive framework with preventative measures, banks can significantly reduce the risk of successful cyberattacks. This includes stronger defenses against malware, phishing attempts, and unauthorized access.
- Improved resilience: The framework encourages proactive measures like vulnerability assessments and penetration testing. This helps banks identify and address weaknesses before they can be exploited, making them more resilient to cyber threats.
- Stronger customer trust: When customers know their bank takes cybersecurity seriously, it builds trust and confidence. Data breaches can seriously damage a bank’s reputation, so the framework helps maintain a secure environment for customer information.
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting the RBI’s cybersecurity framework requirements ensures banks’ compliance with regulations. This avoids potential penalties and demonstrates a commitment to responsible data management.
- Improved incident response: The framework emphasizes developing a Cyber Crisis Management Plan (CCMP). This ensures banks have a clear plan for detecting, containing, and recovering from cyberattacks, minimizing damage and downtime.
- Collective defense: Information sharing is encouraged between banks through the RBI and industry forums. This allows banks to learn from each other’s experiences and stay informed about the latest cyber threats.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, the RBI Guidelines for Cyber Security Framework represent a critical step forward in fortifying the resilience of India’s banking sector against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. By implementing these comprehensive guidelines, financial institutions can significantly enhance their security posture, ensure regulatory compliance, and safeguard customer information. The framework not only equips banks with the tools needed to manage and mitigate cyber risks effectively but also fosters a culture of proactive cybersecurity awareness and preparedness.





